How to plan for a Funding?

To many entrepreneurs looking to start a business and get confused on the best source of funding to seek for their startup. With the many options there are, choosing the ideal source of financing can be an overwhelming process; however, weighing the pros and cons of each source will help you choose the ideal one to go ahead with.
To help you choose the ideal funding source for your business, make sure to review your financial needs, qualifications, and the urgency of financing. Some funding sources need certain requirements to be completed before you qualify. It’s thus important to ensure you are well educated on the various options available to you, and their respective advantages and disadvantages.
But before we should be aware with different kinds of terms used while explaining types funding.
Angel: An angel round is typically a small round designed to get a new company off the ground. Investors in an angel round include individual angel investors, angel investor groups, friends, and family.
Pre-Seed: A Pre-Seed round is a pre-institutional seed round that either has no institutional investors or is a very low amount, often below $150k.
Seed: Seed rounds are among the first rounds of funding a company will receive, generally while the company is young and working to gain traction. Round sizes range between $10k–$2M, though larger seed rounds have become more common in recent years. A seed round typically comes after an angel round (if applicable) and before a company’s Series A round.
Venture – Series Unknown: Venture funding refers to an investment that comes from a venture capital firm and describes Series A, Series B, and later rounds. This funding type is used for any funding round that is clearly a venture round but where the series has not been specified.
Series A and Series B rounds are funding rounds for earlier stage companies and range on average between $1M–$30M.
Series C rounds and onwards are for later stage and more established companies. These rounds are usually $10M+ and are often much larger.
Equity Crowdfunding: Equity crowdfunding platforms allow individual users to invest in companies in exchange for equity. Typically on these platforms the investors invest small amounts of money, though syndicates are formed to allow an individual to take a lead on evaluating an investment and pooling funding from a group of individual investors.
Product Crowdfunding: In a product crowdfunding round, a company will provide its product, which is often still in development, in exchange for capital. This kind of round is also typically completed on a funding platform.
Private Equity: A private equity round is led by a private equity firm or a hedge fund and is a late stage round. It is a less risky investment because the company is more firmly established, and the rounds are typically upwards of $50M.
Convertible Note: A convertible note is an ‘in-between’ round funding to help companies hold over until they want to raise their next round of funding. When they raise the next round, this note ‘converts’ with a discount at the price of the new round. You will typically see convertible notes after a company raises, for example, a Series A round but does not yet want to raise a Series B round.
Debt Financing: In a debt round, an investor lends money to a company, and the company promises to repay the debt with added interest.
Secondary Market: A secondary market transaction is a fundraising event in which one investor purchases shares of stock in a company from other, existing shareholders rather than from the company directly. These transactions often occur when a private company becomes highly valuable and early stage investors or employees want to earn a profit on their investment, and these transactions are rarely announced or publicized.
Grant: A grant is when a company, investor, or government agency provides capital to a company without taking an equity stake in the company.
Corporate Round: A corporate round occurs when a company, rather than a venture capital firm, makes an investment in another company. These are often, though not necessarily, done for the purpose of forming a strategic partnership.
Initial coin offering (ICO): An initial coin offering (ICO) is a means of raising money via crowdfunding using crypto currency as capital. A company raising money through an ICO holds a fundraising campaign, and during this campaign, backers will purchase a percentage of a new crypto currency (called a “token” or “coin”), often using another crypto currency like bitcoin to make the purchase, in the hopes that the new crypto currency grows in value.
Post-IPO Equity: A post-IPO equity round takes place when firms invest in a company after the company has already gone public.
Post-IPO Debt: A post-IPO debt round takes place when firms loan a company money after the company has already gone public. Similar to debt financing, a company will promise to repay the principal as well as added interest on the debt.
Post-IPO Secondary: A post-IPO secondary round takes place when an investor purchases shares of stock in a company from other, existing shareholders rather than from the company directly, and it occurs after the company has already gone public.
Non-Equity Assistance: A non-equity assistance round occurs when a company or investor provides office space or mentorship and does not get equity in return.
Funding Round: “Funding round” is the general term used for a round when information regarding a more specific designation of the funding type is unavailable
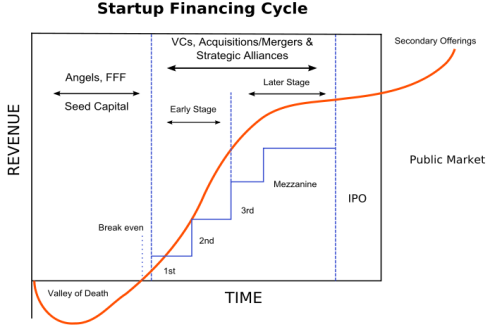
Listed below are some common funding sources, with a brief explanation of each that will help simplify things for you
1. Personal Savings:
This is the most appealing source of financing, because you use your own money to jumpstart your business and don’t owe anyone else in the process.
Pros:
- You have total control of your business, and you may do as you please with your money.
- There’s this satisfaction that you are using your own cash to fund the business.
Cons:
- If the business fails, all the hard work that you had put into your savings will go to waste.
- You may miss out on otherwise valuable guidance and mentorship from angel investors and venture capitalists.
2. Family and Friends:
You can request your friends, family or close associates to help fund your business. This type of funding has more to do with the relationship itself, rather than the assessment of a feasible business plan. The aim of this type of funding is to help kick off a business to a point where it can seek and get other types of funding.
Pros:
- Faster funding process and flexible payment methods.
Cons:
- Family and friends provide the funding without assessing the viability of a business plan itself.
- Brings nothing to the table except for the initial capital investment.
3. Crowdfunding:
This involves funding a business by taking small amounts of capital from a large number of people, usually via the internet. This type of funding makes use of the vast networks you’ve of your friends, family and colleagues via different social platforms to get the word out about the business, with the goal of attracting new investors.
Pros:
- Has the potential of expanding a business by getting a pool of investors who can help raise funds.
Cons:
- Requires time and dedication before results may be realized.
4. Angel Investors:
Angel investors are wealthy individuals who will provide funding in exchange for a share of equity in the business. Some investors work in groups and screen deals together before providing funds, while most work on their own.
Pros:
- Angel investors can offer valuable advice and guidance since they have experience in the industry you’re in.
- Flexible business terms.
Cons:
- You may be forced to give up control of your business to some extent.
5. Venture Capital:
Venture capitalists are investors who put in a considerable amount of money in exchange for equity in the business, and get returns when the business goes public or is acquired by another company. Venture capitalists are all about the money, and only invest in businesses that have the potential of providing good returns on their investment
Pros:
- Venture capitalists not only provide funding, but can offer expertise and mentorship to help develop the business.
- Venture capital funding gives the business immediate credibility and opens other doors to a wide network of important individuals, such as future investors and partners.
Cons:
- You may be forced to give up a large chunk of your business due to the significant amount of funding provided.
6. Bank Loans:
Bank loans are a popular source of funding for many startups. Before applying for a bank loan, it’s important to ensure that you are well educated about the various options available, and the interest rates that come with each option.
Pros:
- There are different funding options depending on your needs.
- The funding process is relatively quick if you qualify.
- You don’t have to give up control of your business.
Cons:
- Requires a lot of documentation, which can be tiring and time-consuming.
- You need educate yourself about the best option available for you; otherwise, you might end up choosing a deal that will eventually hurt your business.
- The money has to be paid back whether the business succeeds or not, failing which may lead to loss of your assets, if any.
7. Small Business Administration (SBA) Loans:
This involves funding from a government administration devoted to assisting small businesses to succeed. SBA’s help small businesses get capital and ensures that a certain percentage of contracts are awarded to the small businesses.
Pros:
- Helps improve the relationship between lenders and borrowers.
- Increased chances of obtaining a bank loan if the SBA loan is properly managed.
Cons:
- Strict qualification guidelines.
Comments
Post a Comment